Головним джерелом накопичення аміаку в організмі людини є окиснювальне дезамінування амінокислот, тобто білковий катаболізм: азот сечовини становить близько 90 % усього азоту, що екскретується. До додаткових джерел утворення аміаку належать: розкладання сечовини й білка уреазапозитивною мікрофлорою шлунково-кишкового тракту, утворення аміаку в м’язовій тканині при фізичному навантаженні, розпад глутаміну в тонкій кишці, абсорбція амонію в нирках при гіпокаліємії і/або алкалозі [1].
Детоксикація аміаку в організмі здійснюється переважно в мітохондріях перипортальних гепатоцитів за рахунок зв’язування в орнітиновому циклі з амінокислотами й утворенням нетоксичної сечовини (рис. 1). Частково детоксикація аміаку відбувається в м’язовій тканині в процесі синтезу глутаміну за участю ферменту глутамінсинтетази. Ця реакція з меншою інтенсивністю відбувається в астроцитах головного мозку й перивенозних гепатоцитах печінки. Кінцевим продуктом цих перетворень є нетоксичний глутамін, який виділяється із сечею [1, 2].
Підвищення вмісту аміаку в крові визначається як гіперамоніємія. Вона розвивається в організмі людини насамперед при хронічних захворюваннях печінки (ХЗП) унаслідок порушення її детоксикуючої функції. До причин цього відносять зниження активності орнітинового циклу й глутамінсинтетазної реакції при печінково-клітинній недостатності й портосистемне шунтування при розвитку й прогресуванні портальної гіпертензії. У свою чергу, це призводить до підвищення концентрації амонію в крові і його подальшого накопичення [3–5].
Гіперамоніємія при ХЗП — це тяжкий стан, який призводить:
— до надмірного накопичення глутаміну в головному мозку, що викликає набухання й набряк астроцитів, пригнічення синтезу гамма-аміномасляної кислоти, порушення трансмембранного переносу електролітів, зниження концентрації α-кетоглутарату, пригнічення трансамінування й синтезу нейромедіаторів. Ці патологічні процеси посилюють гіпоксію і гіпоенергізацію астроцитів, нейронів і призводять до розвитку печінкової енцефалопатії, яка супроводжується підвищеною стомлюваністю, слабкістю, дратівливістю, інверсією сну (сонливість вдень і безсоння вночі), порушенням мовлення, зміною почерку, неуважністю за кермом і при виконанні роботи, що вимагає підвищеної концентрації уваги, тремором, зниженням м’язових рефлексів [8];
— активації зірчастих клітин печінки (ЗКП) і, як наслідок, посиленого колагеноутворення й прогресуючого фіброзування, порушення внутрішньопечінкової гемодинаміки і формування портальної гіпертензії [11];
— саркопенії — протеолізу скелетних м’язів, що підвищує ризик сепсису й смерті при цирозі печінки (ЦП) [9, 10, 12];
— ураження нирок і розвитку ниркової недостатності [11–13].
Усе це обумовлює актуальність проблеми гіперамоніємії і вимагає ранньої діагностики й активної боротьби з нею. Сучасне патогенетичне лікування дозволяє не тільки зупинити прогресування ХЗП, але й іноді — врятувати життя людини.
Нове в патогенезі хронічних захворювань печінки: зірчасті клітини й амоній
Відомо, що в патогенезі хронічних захворювань печінки (хронічних вірусних, алкогольних, лікарських гепатитів, неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки, автоімунних хвороб печінки, генетичних дефектів ферментів орнітинового циклу в печінці) основною ланкою в розвитку запалення й фіброзу є активація зірчастих клітин.
Зірчасті клітини, або клітини Іто, — це клітини, які накопичують жир у певній ділянці печінки, відомій як перисинусоїдальний простір, або простір Діссе, і з цієї причини вони також відомі як печінкові ліпоцити. Тіло зірчастої клітини має видовжену форму з ядрами овальної або витягнутої форми. Окрім того, що в ньому містяться крихітні крапельки вітаміну А, у цитоплазмі знаходяться невеликий комплекс Гольджі поблизу ядра і добре розвинений ендоплазматичний ретикулум. Зірчасті клітини виробляють широкий спектр білків цитоскелета й сполучної тканини, таких як дезмін, віментин, актин, тубулін, фібронектин, колаген і ламінін [12].
У дослідженні R. Jalan et al. було показано, що активація зірчастих клітин також обумовлена гіперамоніємією, яка призводить до посиленого колагеноутворення й прогресуючого фіброзування [9]. Зірчасті клітини диференціюються в міофібробластоподібні клітини, які набувають скоротливих, прозапальних і фіброгенетичних властивостей. При цьому ЗКП проліферують, з них зникають краплі жиру, збільшується ендоплазматична мережа, з’являється специфічний білок гладеньких м’язів (α-актин) і збільшується кількість рецепторів до цитокінів, що стимулюють проліферацію і фіброгенез.
Активовані ЗКП мігрують і акумулюються в місці ураження тканини печінки, при цьому секретують велику кількість позаклітинного матриксу й одночасно регулюють деградацію цих молекул на рівнях транскрипції і посттранскрипції. Підвищення вмісту інформаційної колагенової РНК є опосередковуючим фактором, що підвищує синтез колагену активованими ЗКП. Крім цього, ЗКП експресують велику кількість нейроендокринних маркерів (релін, нестин, нейротрофіни, синаптофізин і гліально-фібрилярні кислотні протеїни). ЗКП несуть рецептори нейротрансмітерів, виділяють прозапальні цитокіни, нейрофільний і моноцитарний хемоатрактани, які посилюють запальну реакцію в ураженій печінці [15].
Фіброз печінки є основним, етіологічно незалежним шляхом прогресування хронічних дифузних захворювань печінки, навіть до цирозу. Він асоціюється зі зміною кількісного і якісного складу екстрацелюлярного колагенового матриксу (ЕКМ). При виражених стадіях фіброзу печінка містить приблизно в 6 разів більше ЕКМ, ніж у нормі, а в його складі визначаються колагени 1, 3 і 4 типів, фібронектин, ундулін, еластин, ламінін, гіалуронан і протеоглікани. Зниження швидкості резорбції ЕКМ і виведення молекул металопротеїназ є в основному наслідком вивільнення їх специфічних інгібіторів. Результатом превалювання процесів утворення позаклітинного матриксу над його руйнуванням є формування фіброзного рубця, при цьому фіброз на ранніх стадіях розвитку — процес оборотний, а цироз із характерними зшивками між колагеновими волокнами і вузлами регенерації — необоротний. Прогресуюче накопичення й відкладання позаклітинного матриксу в просторі Діссе призводять до зникнення фенестрів ендотелію, капіляризації і стенозування синусоїдів з поступовим розвитком портальної гіпертензії [16–18].
У дослідженні R. Jalan et al. [9] було виявлено, що додатковим фактором ризику портальної гіпертензії при гіперамоніємії є нітрозативний стрес, що є причиною порушень печінкової гемодинаміки. При цьому спостерігається збільшення білкової експресії показників нітрозативного стресу: індукованої NO-синтази (iNOS), ендотеліальної NO-синтази (eNOS), кавеоліну-1 (внутрішньоклітинного інгібітора eNOS) і 3-N-тирозину. При застосуванні орнітину спостерігалось знижування експресії iNOS, кавеоліну-1 і 3-N-тирозину і відновлення ферментативної активності eNOS [9].
Отже, за наявності ХЗП і гіперамоніємії формується порочне коло: пошкодження печінки призводить до збільшення вмісту амонію, а підвищення рівня амонію викликає патологічні зміни в зірчастих клітинах людини, порушує внутрішньоклітинну гемодинаміку, збільшує портальну гіпертензію, посилює формування фіброзу печінки, що призводить до прогресування хронічних захворювань печінки.
Тому гіперамоніємія є мішенню для лікування ХЗП [9].
Гепа-Мерц у лікуванні хронічних захворювань печінки для зменшення гіперамоніємії і створення передумов для відновлення функцій і цілісності печінки
Зниження рівня аміаку є патогенетичним підходом до лікування ХЗП, що дозволяє зменшувати клінічні прояви захворювання й активацію ЗКП, покращувати печінковий кровотік і перешкоджати розвитку й прогресуванню фіброзу печінки. З цією метою пріоритетним напрямком є застосування оригінального L-орнітин-L-аспартату (LOLA; Гепа-Мерц), стабільної солі орнітину й аспарагінової кислоти, яка забезпечує подвійний механізм детоксикації амонію: зв’язування аміаку в орнітиновому циклі сечовиноутворення в печінці (основний шлях) і зв’язування токсину з глутаматом з утворенням глутаміну в печінці, м’язовій тканині й клітинах астроглії головного мозку [19, 21].
Орнітин і аспартат — попередники аргініну в циклі Кребса, донатора оксиду азоту, який покращує функцію ендотелію; знижує рівень аміаку в крові, що сприяє деактивації зірчастих клітин печінки і зменшує їх контрактильність, збільшує активність eNOS, впливаючи на внутрішньопечінковий кровотік; покращує функції гепатоцитів за рахунок покращення енергетичних процесів (синтезу АТФ), регенерації гепатоцитів, синтезу білка. У свою чергу, деактивація ЗКП, підвищення активності eNOS, продукція оксиду азоту в судинах печінки гальмують розвиток фіброзу печінки [20].
Також важливим ефектом препарату є посилення бета-окиснення жирних кислот у мітохондріях, зниження якого є одним з провідних патогенетичних факторів формування надлишку вільних жирних кислот і відкладення їх у печінці [26]. Орнітин відіграє важливу роль у синтезі поліамінів (спермін, спермідин, путресцин) — біологічно активних речовин, що регулюють синтез білка, ріст і диференціацію клітин, а також продукцію енергетичних субстанцій (нікотинамідаденіндинуклеотидфосфат — НАДФ) [31]. Аспартат чинить безпосередню цитопротекторну дію на гепатоцити, запобігаючи зниженню внутрішньоклітинної концентрації АТФ в уражених гепатоцитах і викиду трансаміназ із гепатоцитів, зменшуючи таким чином пошкодження тканини печінки [32].
Доведено, що гепатопротекторна дія Гепа-Мерц реалізується за рахунок його метаболітів. Із L-орнітину-L-аспартату утворюється L-глутамат, який під впливом ферментів розпадається на L-глутамін і глутатіон. Останній є антиоксидантом і зменшує гепатоцелюлярне пошкодження (трансаміназний шлях). З L-аргініну утворюється оксид азоту, який покращує мікроциркуляцію в печінці (цикл сечовини) (рис. 2).
Гепа-Мерц — доведена ефективність і безпека в лікуванні гіперамоніємії при хронічних захворюваннях печінки
На сьогодні накопичена велика доказова база контрольованих випробувань, що підтверджують високу ефективність і добру переносимість препарату Гепа-Мерц у пацієнтів із ХЗП.
Наростання концентрації аміаку виявляється у хворих на ХЗП вже на доциротичній стадії, що потребує зниження його рівня. У дослідженні за участю хворих на неалкогольну жирову хворобу печінки показано, що на тлі застосування L-орнітину-L-аспартату гіперамоніємія, яка початково була на 0–1 стадії фіброзу, істотно знизилася, що супроводжувалося покращанням загального стану й лабораторних показників [6]. Лікування 289 пацієнтів з неалкогольним стеатогепатитом з використанням LOLA протягом трьох місяців на тлі доброї переносимості й високої прихильності хворих сприяло зниженню рівнів аміаку, що корелює зі зменшенням судинних порушень, статистично значущим покращанням клініко-біохімічних показників і якості життя [7].
Рандомізоване подвійне сліпе плацебо-контрольоване дослідження ефективності інфузійної форми випуску препарату Гепа-Мерц за участю 126 пацієнтів з цирозом печінки, гіперамоніємією (> 50 мкмоль/л) і печінковою енцефалопатією (ПЕ) (латентної, I і II ступеня) було виконано G. Kircheis et al. [22, 23]. 63 учасникам основної групи протягом 14 діб проводили внутрішньовенні інфузії препарату Гепа-Мерц у дозі 20 г/добу, а 63 хворим групи плацебо — інфузії 5% розчину фруктози. У пацієнтів, які отримували Гепа-Мерц паралельно з білковим навантаженням, порівняно з групою плацебо відзначена позитивна динаміка в плані корекції порушень функції печінки — зниження постпрандіального і рівня аміаку натще у венозній крові. Паралельно спостерігали значний прогрес щодо когнітивних функцій — при оцінці тесту зв’язку чисел, індексу системної ПЕ (Portal Systemic Encephalopathy Index — PSEI), шкали оцінювання психічного статусу (Mental State Grade — MSG).
Незначні гастроінтестинальні симптоми, які не потребували відміни препарату, відзначали у 3 (5 %) хворих, які отримували Гепа-Мерц. Повідомлень про інші побічні ефекти, пов’язані з препаратом Гепа-Мерц, не надходило, що дозволило авторам дослідження дійти висновку про високу безпеку й ефективність препарату Гепа-Мерц при лікуванні пацієнтів з ЦП і ПЕ.
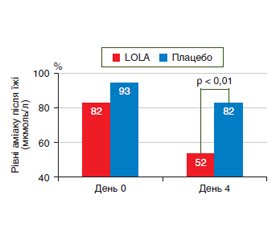
Подібні дані отримані й щодо пероральної форми випуску препарату Гепа-Мерц в ще одному дослідженні аналогічного дизайну, учасниками якого стали 66 пацієнтів із ЦП, гіперамоніємією і хронічною ПЕ, у тому числі латентною [33]. 34 хворі основної групи отримували Гепа-Мерц по 18 г/добу перорально протягом 14 діб, а 32 хворі становили групу плацебо. Протеїнове навантаження розраховували виходячи з маси тіла пацієнта (0,25 г/кг маси тіла на добу). За підсумками дослідження встановлена значуща ефективність препарату Гепа-Мерц щодо покращання функції печінки — істотне зниження постпрандіального й рівня аміаку натще у венозній крові вже на 4-й день лікування (рис. 3), зменшення печінкової інтоксикації і ПЕ (позитивна динаміка когнітивних тестів — зв’язку чисел і PSEI, MSG).
У пацієнтів, які отримували Гепа-Мерц, на відміну від групи плацебо до 14-ї доби була досягнута нормалізація рівня аміаку натще. Побічних ефектів у процесі дослідження не відзначено. Автори даного дослідження оцінили Гепа-Мерц як ефективний і безпечний препарат, а також відзначили високий комплаєнс пацієнтів.
K. Grungreiff et al. [27] опублікували результати великого дослідження з оцінки ефективності й переносимості препарату Гепа-Мерц, проведеного на базі 250 медичних установ вузького й широкого профілю (Німеччина). Учасниками його стали 1167 пацієнтів з переважно хронічною патологією печінки (ЦП, жирова дистрофія, гострий і хронічний гепатит) і ПЕ віком 18–87 років. Що стосується етіологічної характеристики патології печінки в цій групі хворих, то в 71 % випадків основне захворювання було викликане зловживанням алкоголем, у 20 % — вірусними інфекціями, в 10,5 % — побічною дією лікарських засобів, у 4 % — впливом хімічних токсинів на виробництві.
За допомогою терапії препаратом Гепа-Мерц вдалося досягти значущого покращання в пацієнтів з ЦП (зниження рівнів трансаміназ у середньому на 35 %, гамма-глутамілтранспептидази (ГГТП) — на 50 %), стеатозом печінки (зниження рівня трансаміназ і ГГТП на ≈ 50 %), хронічним гепатитом (зниження рівня трансаміназ і ГГТП на 40–50 %) (рис. 4).
Крім того, на тлі застосування препарату Гепа-Мерц у 49 % хворих зі слабо вираженою ПЕ вдалося повністю усунути ознаки печінкової енцефалопатії. У 78 % хворих з явною ПЕ також відзначали позитивну динаміку, що підтверджує клінічну ефективність препарату Гепа-Мерц при ПЕ на різних стадіях.
37 % лікарів, які брали участь у дослідженні, оцінили терапевтичну ефективність препарату Гепа-Мерц як дуже добру, 50 % — як добру. На думку лікарів, стан 45 % хворих, які пройшли курс лікування препаратом Гепа-Мерц, істотно покращився, 46 % — покращився.
У 73 % випадків переносимість препарату була описана лікарями як дуже добра, у 25 % — як добра. Побічні дії фіксувались в 1,6 % випадків, частіше у вигляді диспептичних явищ; при цьому більшість цих пацієнтів змогли продовжити лікування без відміни препарату.
У дослідженні, проведеному в Китаї, брали участь 85 пацієнтів із цирозом печінки: 45 — основна група, 40 — контрольна група. На тлі стандартної комплексної терапії пацієнти основної групи отримували щодня 40 мл оригінального L-орнітину-L-аспартату внутрішньовенно. Було визначено, що, крім зниження активності трансаміназ у сироватці, у пацієнтів також підтримувався рівень АТФ у гепатоцитах і спостерігалася сприятлива дія на функціонування цих клітин [34].
У відкритому проспективному багатоцентровому дослідженні Ong et al. (2011) оцінювали вплив Гепа-Мерц на інші показники якості життя пацієнтів із ЦП і ПЕ. Після 8 тижнів перорального лікування Гепа-Мерц у добовій дозі 6 г спостерігали виражене покращання всіх доменів шкали HR-QOL, особливо втоми (на 67,5 %) (рис. 5). Крім того, в пацієнтів значно зменшилася тяжкість абдомінальних симптомів, покращилися сон і когнітивна функція. Високу або дуже високу ефективність Гепа-Мерц у кінці лікування відзначили в 70 % пацієнтів, добру або дуже добру переносимість — у 97,8 % хворих.
/65.jpg)
E.T. Goh et al. у метааналізі, який включав 29 рандомізованих клінічних досліджень і 1893 пацієнти з ХЗП і ПЕ, порівнювали L-орнітин-L-аспартат з плацебо або відсутністю втручання; L-орнітин-L-аспартат порівнювали з іншими активними агентами, такими як дисахариди, антибіотики, пробіотики або амінокислоти з розгалуженим ланцюгом. Аналіз продемонстрував, що L-орнітин-L-аспартат може знизити смертність, зменшити прояви печінкової енцефалопатії і запобігти розвитку серйозних побічних ефектів порівняно з плацебо або відсутністю лікування [28].
М. Bai et al. [18] повідомили про вірогідний ефект препарату Гепа-Мерц при гіперамоніємії, викликаній транс’югулярним внутрішньопечінковим портосистемним шунтуванням у пацієнтів із цирозом печінки. У пацієнтів, які отримували Гепа-Мерц, було відзначено більш виражене зменшення рівня аміаку в 1, 4 і 7-й дні спостереження порівняно з пацієнтами контрольної групи. Протягом усього дослідження пацієнти, які лікувалися препаратом Гепа-Мерц, демонстрували виражене покращання психічних функцій на відміну від пацієнтів, які отримували плацебо.
Подвійне сліпе рандомізоване плацебо-контрольоване дослідження S.S. Sidhu et al. [25] за участю 193 пацієнтів показало вірогідну перевагу 5-денного курсу внутрішньовенного введення LOLA Гепа-Мерц у дозі 30 г на день над плацебо (як стандартну терапію пацієнти основної і контрольної груп отримували лактулозу й цефтріаксон).
У дослідженні Alvares-da-Silva et al. [29] було доведено, що призначення перорального прийому Гепа-Мерц у щоденній дозі 5 г порівняно з плацебо протягом 60 днів має здатність запобігати новим нападам енцефалопатії.
Велика доказова база ефективності Гепа-Мерц при печінковій енцефалопатії, асоційованій з гіперамоніємією, стала основою для включення препарату з 2014 р. у рекомендації Європейської (EASL) та Американської (AASLD) асоціацій з вивчення захворювань печінки для лікування печінкової енцефалопатії [30].
Висновки
— При хронічних захворюваннях печінки формується й наростає гіперамоніємія як наслідок порушення її детоксикуючої функції. Це обумовлено зниженням активності орнітинового циклу й глутамінсинтетазної реакції при печінково-клітинній недостатності й портосистемним шунтуванням у разі розвитку й прогресування портальної гіпертензії.
— Гіперамоніємія викликає мультиорганну дисфункцію: індукує окиснювальний стрес, ендотеліальну дисфункцію, індуцибельну ізоформу синтази оксиду азоту, активує зірчасті клітини печінки, викликає апоптоз гепатоцитів, ураження нирок і саркопенію (протеоліз скелетних м’язів).
— Порочне коло змін при ХЗП: пошкодження печінки призводить до збільшення вмісту амонію, а підвищення рівня амонію викликає патологічні зміни в зірчастих клітинах людини, порушує внутрішньоклітинну гемодинаміку, збільшує портальну гіпертензію, посилює формування фіброзу печінки, що призводить до прогресування хронічних захворювань печінки. Тому гіперамоніємія є важливою мішенню для лікування ХЗП.
— Пріоритетним напрямком у боротьбі з гіперамоніємією є застосування оригінального L-орнітину-L-аспартату (Гепа-Мерц), стабільної солі орнітину й аспарагінової кислоти, яка забезпечує подвійний механізм детоксикації амонію: зв’язування аміаку в орнітиновому циклі сечовиноутворення в печінці (основний шлях) і зв’язування токсину з глутаматом з утворенням глутаміну в печінці, м’язовій тканині й клітинах астроглії головного мозку.
— Гепатопротекторна дія Гепа-Мерц реалізується за рахунок його метаболітів. З L-орнітину-L-аспартату утворюється L-глутамат, який під впливом ферментів розпадається на L-глутамін і глутатіон. Останній, будучи антиоксидантом, зменшує гепатоцелюлярне пошкодження (трансаміназний шлях). З L-аргініну утворюється оксид азоту, який покращує мікроциркуляцію в печінці (цикл сечовини).
— Численні контрольовані випробування підтверджують високу ефективність і добру переносимість препарату Гепа-Мерц у пацієнтів при ХЗП. Доведено, що призначення Гепа-Мерц знижує рівень аміаку й трансаміназ, покращує клінічний стан пацієнтів, запобігає прогресуванню ХЗП.
— Велика доказова база ефективності оригінального LOLA при печінковій енцефалопатії, асоційованій з гіперамоніємією, стала основою для включення препарату в 2014 р. у рекомендації Європейської (EASL) та Американської (AASLD) асоціацій з вивчення захворювань печінки для лікування печінкової енцефалопатії.
UA-HEME-PUB-102022-021
/62_4.jpg)
/63.jpg)
/64.jpg)

/65.jpg)