Журнал «Боль. Суставы. Позвоночник» Том 15, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Наш досвід ревізійного ендопротезування кульшового суглоба
Авторы: Полулях М.В. (1), Герасименко С.І. (1), Полулях Д.М. (1), Герасименко А.С. (1), Бабко А.М. (1), Басманов С.М. (2), Ярош Д.С. (2)
(1) - ДУ «Національний інститут травматології та ортопедії НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
(2) - Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Ревматология, Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
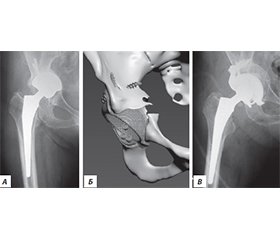
Актуальність. Ендопротезування кульшового суглоба сьогодні є одним із найбільш поширених і водночас ефективних методів лікування. Проте у віддалені терміни після операції виникає проблема розвитку нестабільності елементів протеза, що потребує повторних оперативних втручань, які належать до категорії складних і технічно трудомістких. Мета дослідження: на основі власного досвіду ревізійного ендопротезування кульшового суглоба та даних літератури обговорити питання планування і вибору тактики оперативного лікування для покращення результатів. Матеріали та методи. Було проаналізовано результати 146 ревізійних ендопротезувань кульшового суглоба у пацієнтів з асептичною нестабільністю елементів протеза за 11 років (2012–2022). Серед обстежених було 93 жінки та 53 чоловіки, вік пацієнтів коливався від 24 до 82 років (середній вік становив 64,5 року). Функціональне відновлення хворих оцінювали за шкалою Harris Hip Score. Результати. Нестабільність ацетабулярного компонента й ніжки протеза спостерігали у 34 пацієнтів, лише ацетабулярного компонента — у 48 осіб, лише ніжки — у 32 хворих, вивих протеза — у 9, стирання поліетиленового вкладиша — у 5, перелом керамічної головки — у 2, перелом ніжки протеза — в 1, перипротезні переломи — у 15 пацієнтів. Середній показник шкали Harris Hip Score становив 79,3 бала (95% довірчий інтервал: 73,9–84,7). Відмінні або добрі результати досягнуто у 52,8 % пацієнтів, задовільні — у 29,5 %, незадовільні — у 17,8 %. Загальна частота післяопераційних ускладнень становила 7,53 %. Висновки. У ревізійному ендопротезуванні доцільно віддавати перевагу безцементним системам фіксації з обов’язковим застосуванням кісткової пластики при дефіциті кісткової тканини. Найбільш ефективними виявилися ацетабулярні чашки з покриттям екструдованим титаном, а також ревізійні й індивідуально виготовлені конструкції. При ревізії стегнового компонента ніжка Wagner продемонструвала стабільні клінічні результати та надійність фіксації.
Background. Hip arthroplasty is one of the most common and effective surgical methods of treatment. However, over time, the problem of prosthetic component instability arises, requiring revision procedures. The aim was to analyze own experience of revision hip arthroplasty and literature data, with a focus on planning and surgical strategy to improve outcomes. Materials and methods. We analyzed the results of 146 revision hip arthroplasties performed in patients with aseptic prosthetic component instability in 2012–2022. The study cohort included 93 women and 53 men, aged 24–82 years (mean age 64.5). The functional recovery of patients was assessed using the Harris Hip Score scale. Results. Instability of both the acetabular component and femoral stem was observed in 34 patients; isolated acetabular component instability in 48; isolated femoral stem instability in 32; prosthetic dislocation in 9; polyethylene liner wear in 5; ceramic head fracture in 2; femoral stem fracture in 1; and periprosthetic fractures in 15 patients. The mean Harris Hip Score was 79.31 units (95% CI: 73.9–84.7). More than half of the patients (52.8 %) achieved excellent or good results, 29.5 % — satisfactory, and 17.8 % — unsatisfactory. The overall rate of postoperative complications was 7.53 %. Conclusion. In revision hip arthroplasty, preference should be given to cementless fixation systems with mandatory bone grafting in cases of bone deficiency. The most effective implants were acetabular cups with extruded titanium coating, as well as revision and custom-made components. In femoral component revisions, the Wagner stem demonstrated stable clinical outcomes and reliable fixation.
ревізійне ендопротезування; кульшовий суглоб; нестабільність ніжки протеза; нестабільність ацетабулярного компонента; кісткова пластика
revision; hip arthroplasty; femoral stem instability; acetabular component instability; bone grafting