Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Депресія, тривога, стрес та рівень глікозильованого гемоглобіну в підлітків із цукровим діабетом 1-го типу
Авторы: Alif Mutahhar, Nur Rochmah, Muhammad Faizi
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Dr. Soetomo General Academic Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
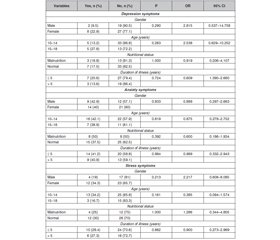
Актуальність. Лікування цукрового діабету 1-го типу (ЦД1) потребує тривалої інсулінотерапії. Це може призвести до проблем із психічним здоров’ям, як-от депресія, тривога й стрес, погіршуючи глікемічний контроль, про що свідчать рівні глікозильованого гемоглобіну (HbA1c), та загалом до поганих наслідків. Шкала депресії, тривоги й стресу (DASS) є одним із інструментів для скринінгу таких симптомів. Мета: оцінити поширеність ознак депресії, тривоги й стресу і кореляцію між балами за шкалою DASS та рівнем HbA1c у підлітків із ЦД1. Матеріали та методи. Поперечне дослідження проведено з червня по грудень 2023 року за участю пацієнтів віком 10–18 років із ЦД1. Для оцінки симптомів депресії, тривожності та стресу використовували шкалу DASS-21. Дані аналізували за допомогою програмного забезпечення Statistical Package for the Social Sciences версії 22. Результати. У цьому дослідженні взяли участь 56 підлітків із ЦД1 віком 10–18 років. Більшість становили дівчата, середній вік пацієнтів дорівнював 13,5 року. Найчастіше спостерігався нормальний харчовий статус, а тривалість захворювання переважно була менше п’яти років. Середній рівень HbA1c дорівнював 10,2 %. Поширеність симптомів депресії, тривоги й стресу становила відповідно 17,8; 41,1 та 28,6 %. Не помічено вірогідної кореляції між будь-якою підшкалою DASS (депресія, тривога та стрес) та рівнями HbA1c. Висновки. Тривога була найпоширенішим симптомом, хоча зв’язку між оцінкою за шкалою DASS та вмістом HbA1c у підлітків із цукровим діабетом 1-го типу не виявлено. Ранній та регулярний моніторинг щодо психічних проблем у підлітків із цукровим діабетом 1-го типу має вирішальне значення для поліпшення результатів лікування діабету.
Background. Management of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) requires long-term insulin therapy, which can lead to mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and stress, worsening glycemic control, as demonstrated by glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, and poor outcomes. The Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scale (DASS) is one of the instruments for screening these symptoms. This study purposed to assess the prevalence of depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms and correlation between DASS score and HbA1c levels in adolescents with T1DM. Materials and methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted from June to December 2023 involving pediatric patients aged 10–18 years with T1DM. This research employed the DASS-21 questionnaire to measure depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms, with data analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 22 software. Results. The study involved 56 adolescents with T1DM aged 10–18. The majority were females, with a median age of 13.5 years. Normal nutritional status was the most common, and duration of illness was predominantly less than five years. The mean HbA1c level was 10.2 %. The prevalence of depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms was 17.8, 41.1, and 28.6 %, respectively. No significant correlation was found between any DASS subscales (depression, anxiety, and stress) and HbA1c levels. Conclusions. Anxiety was the most common symptom, even though no correlation was found between DASS and HbA1c levels among adolescents with T1DM. Early and regular screening of mental issues in adolescents with T1DM is critical for improving diabetes management outcomes.
тривога; депресія; цукровий діабет 1-го типу; HbA1c; стрес
anxiety; depression; type 1 diabetes mellitus; HbA1c; stress
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Zheng C, Yin J, Wu L, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Cao L, Qu Y. Association between depression and diabetes among American adults using NHANES data from 2005 to 2020. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):27735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78345-y.
- Franquez RT, de Souza IM, Bergamaschi CC. Interventions for depression and anxiety among people with diabetes mellitus: review of systematic reviews. PLoS One. 2023;18(2):e0281376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281376.
- Tripathi P, Sharma B, Kadam N, Tiwari D, Kathrikolly T, Vyawahare A, et al. Improvement in symptoms of anxiety and depression in individuals with type 2 diabetes: retrospective analysis of an intensive lifestyle modification program. BMC Psychiatry. 2024;24(1):714. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06130-2.
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ; IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2021.
- Pulungan A. Increasing incidence of DM type 1 in Indonesia. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013;2013(Suppl 1):O12. doi: 10.1186/1687-9856-2013-S1-O12.
- Respati GDP, Faizi M, Pranoto A, Andarsini MR. Clinical profile of type-1 diabetes pediatric patients in Dr. Soetomo General Academic Hospital Surabaya: correlation of growth status and metabolic control. Maj Biomorfologi. 2023;33(1):7-13. doi: 10.20473/mbiom.v33i1.2023.7-13.
- Dahlquist G, Källén B. Mortality in childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: a population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(10):2384-2387. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.10.2384.
- Buchberger B, Huppertz H, Krabbe L, Lux B, Mattivi JT, Siafarikas A. Symptoms of depression and anxiety in youth with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;70:70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.04.019.
- Déniz-García A, Díaz-Artiles A, Saavedra P, Alvarado-Martel D, Wägner AM, Boronat M. Impact of anxiety, depression and disease-related distress on long-term glycaemic variability among subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01013-7.
- Covic T, Cumming SR, Pallant JF, Manolios N, Emery P, Conaghan PG, Tennant A. Depression and anxiety in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence rates based on a comparison of the Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-6.
- Moya E, Larson LM, Stewart RC, Fisher J, Mwangi MN, Phiri KS. Reliability and validity of Depression Anxiety Stress Scale –(DASS)-21 in screening for common mental disorders among postpartum women in Malawi. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03994-0.
- Cao CH, Liao XL, Jiang XY, Li XD, Chen IH, Lin CY. Psychometric evaluation of the Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale-21 –(DASS-21) among Chinese primary and middle school teachers. BMC Psychol. 2023;11(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01242-y.
- Chen IH, Chen CY, Liao XL, Chen XM, Zheng X, Tsai YC, et al. Psychometric properties of the Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale (DASS-21) among different Chinese populations: a cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2023;240:104042. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2023.104042.
- Andreoulakis E, Hyphantis T, Kandylis D, Iacovides A. Depression in diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review. Hippokratia. 2012;16(3):205-214.
- Kaur G, Tee GH, Ariaratnam S, Krishnapillai AS, China K. Depression, anxiety and stress symptoms among diabetics in Malaysia: a cross-sectional study in an urban primary care setting. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-14-69.
- Bener A, Ozturk M, Yildirim E. Association between depression, anxiety and stress symptoms and glycemic control in diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Clin Endocrinol. 2017;1(1):1-7.
- Hakim MA, Aristawati V. Measuring depression, anxiety, and stress in early adults in Indonesia: Construct validity and reliability test of DASS-21. J Psikol Ulayat. 2023;10(2):232-250. doi: 10.24854/jpu553.
- Fisekovic Kremic MB. Factors associated with depression, anxiety and stress among patients with diabetes mellitus in primary health care: many questions, few answers. Malays Fam Physician. 2020;15(3):54-61.
- Ludiana L, Hasanah U, Sari SA, Fitri NL, Nurhayati S. Hubungan faktor psikologis (stres dan depresi) dengan kadar gula darah penderita diabetes mellitus tipe 2. J Wacana Kesehatan. 2022;7(2):61. doi: 10.52822/jwk.v7i2.413.
- Egede LE, Osborn CY. Role of motivation in the relationship between depression, self-care, and glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36(2):276-283. doi: 10.1177/0145721710361389.
- Kendzor DE, Chen M, Reininger BM, Businelle MS, Ste–wart DW, Fisher-Hoch SP, et al. The association of depression and anxiety with glycemic control among Mexican Americans with diabetes li–ving near the US-Mexico border. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:176. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-176.
- Silina E, Taube M, Zolovs M. Exploring the mediating role of parental anxiety in the link between children’s mental health and glycemic control in type 1 diabetes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(19):6849. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20196849.
- Patton SR, Kahhan N, Pierce JS, Benson M, Fox LA, Cle–ments MA. Parental diabetes distress is a stronger predictor of child HbA1c than diabetes device use in school-age children with type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023;11(5):e003607. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003607.
- McInerney AM, Lindekilde N, Nouwen A, Schmitz N, Deschênes SS. Diabetes distress, depressive symptoms, and anxiety symptoms in people with type 2 diabetes: a network analysis approach to understanding comorbidity. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(8):1715-1723. doi: 10.2337/dc21-2297.
- Pulungan AB, Annisa D, Imada S. Type 1 diabetes mellitus in children: Indonesian situation and management. Sari Pediatri. 2019;20(6):392-400. doi: 10.14238/sp20.6.2019.392-400.
- Tatti P, Pavandeep S. Gender difference in type 1 diabetes: an underevaluated dimension of the disease. Diabetology. 2022;3(2):364-368. doi: 10.3390/diabetology3020027.
- Indriyani R, Tjahjono HA. Relationship between glycemic, vitamin D and nutrition status control in children with type 1 diabetes. J Kedokteran Brawijaya. 2018;30:114-120. doi: 10.21776/ub.jkb.2018.030.02.7.
- Rochmah N, Perwitasari RK, Hisbiyah Y, et al. Factors affecting insulin-like growth factor-1 in type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. J Med Pharm Chem Res. 2024;7(1):120-128. doi: 10.48309/jmpcr.2025.451173.1185.
- Pulungan AB, Fadiana G, Annisa D. Type 1 diabetes mellitus in children: experience in Indonesia. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021;30(1):11-18. doi: 10.1297/cpe.30.11.