Международный неврологический журнал Том 21, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Досвід лікування спастичності у дітей з органічними ураженнями центральної нервової системи
Авторы: Сухоносова О.Ю. (1), Коренєв С.М. (1), Сальникова В.В. (2)
(1) - Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
(2) - КНП «Міська дитяча лікарня № 5» Харківської міської ради, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Неврология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
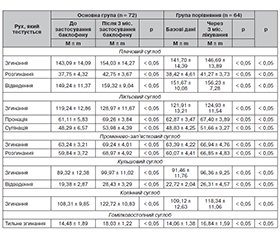
Актуальність. Спастичність є одним із найпоширеніших проявів порушення тонусу м’язів у дітей із неврологічними розладами, зокрема при дитячому церебральному паралічі. Кількість цих інвалідизуючих захворювань зростає з кожним роком. Реабілітація направлена на зменшення ступеня рухових порушень, підвищення функціональної активності дитини, зменшення больових відчуттів, полегшення догляду за дитиною та запобігання ортопедичним ускладненням. Мета: оцінити ефективність застосування баклофену у комплексній реабілітації дітей з руховими порушеннями внаслідок органічного ураження ЦНС. Матеріали та методи. Під нашим наглядом перебувало 136 дітей віком від 4 до 18 років, які мали рухові порушення внаслідок органічного ураження ЦНС. Дітей було розподілено на 2 групи: 1-ша (основна) група — 72 хворі (52,94 %), які отримували баклофен протягом 3 місяців та реабілітаційні заходи, та 2-га (контрольна) група — 64 хворі (47,06 %), які отримували лише реабілітаційні заходи. Результати. Аналіз впливу препарату на рівень м’язового тонусу за даними неврологічного статусу, рухову активність за даними стандартизованих шкал (класифікації великих моторних функцій — GMFCS, класифікації виконання функцій руками (MACS), оцінки м’язового тонусу за шкалою Ашворса) та загальної ефективності комплексної реабілітаційної терапії (вимірювання об’єму рухів у суглобах кінцівок з використанням гоніометра) показав вірогідне поліпшення стану хворих. Отримані результати після застосування баклофену у дітей зі спастичними парезами та паралічами внаслідок органічних уражень ЦНС дозволяють вважати, що баклофен може бути рекомендований до застосування у загальній клінічній практиці як обґрунтована складова комплексної терапії хворих з вираженими генералізованими порушеннями м’язового тонусу. Висновки. Отримані результати підтверджують доцільність використання баклофену як складової фармакологічної корекції спастичного синдрому у дитячому віці.
Background. Spasticity is one of the most common manifestations of muscle tone disorders in children with neurological disorders, including cerebral palsy. The number of these disa-bling diseases is increasing every year. Rehabilitation is aimed at reducing the degree of motor disorders, increasing the functional activity of a child, reducing pain, facilitating childcare and preventing orthopedic complications. The purpose was to assess the effectiveness of baclofen in the comprehensive rehabilitation of children with motor disorders due to organic CNS lesions. Materials and methods. We monitored 136 children aged 4 to 18 years who had motor disorders due to organic CNS lesions. They were divided into 2 groups: group 1 (main) — 72 patients (52.94 %) who received baclofen for 3 months and rehabilitation measures and group 2 (controls) — 64 children (47.06 %) who received only rehabilitation measures. Results. Analysis of the drug effect on the level of muscle tone according to neurological status, motor activity according to standardized scales (the Gross Motor Function Classification System, the Manual Ability Classification System, assessment of muscle tone according to the Modified Ashworth Scale) and the overall effectiveness of comprehensive rehabilitation therapy (measurement of the range of movements in the limb joints using a goniometer) showed a significant improvement in the patients’ state. The results obtained after the use of baclofen in children with spastic paresis and paralysis due to organic lesions of the CNS allow us to believe that baclofen can be recommended for use in general clinical practice as a justified component of comprehensive therapy of patients with generalized severe muscle tone disorders. Conclusions. The obtained results confirm the feasibility of using baclofen as a component of pharmacological correction for spastic syndrome in childhood.
спастичність; органічне ураження ЦНС; діти; реабілітація; медикаментозна терапія; баклофен; м’язовий тонус
spasticity; organic lesions of the CNS; children; rehabilitation, drug therapy; baclofen; muscle tone