Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №3, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Інтервенція на основі SMS-повідомлень для поліпшення показників вакцинації дітей: попередні результати пілотного проєкту в громадах iз низьким рівнем явки на вакцинацію у Львівській області
Авторы: Ye.O. Grechukha (1), N.M. Kolachynskyi (2), N.O. Ivanchenko (2), A.V. Kovalchuk (3), A.P. Volokha (1), G.V. Gnyloskurenko (4)
(1) - Shupyk National Healthcare University of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
(2) - Lviv Regional Center for Disease Control and Prevention of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, Lviv, Ukraine
(3) - WHO Country Office in Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
(4) - Institute of Biology and Medicine, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
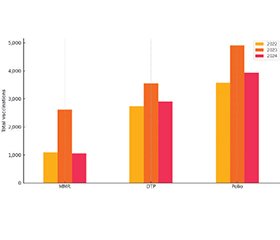
Актуальність. Цифрові втручання в охороні здоров’я, зокрема сповіщення через SMS-повідомлення, мають значний потенціал щодо поліпшення медичних результатів, включаючи рівень вакцинації. Конфлікт в Україні та порушення роботи медичної інфраструктури підвищили актуальність пошуку інноваційних підходів для підтримки планових послуг з імунізації. Мета: оцінити здійсненність та ефективність інтервенції з використанням SMS-повідомлень для підвищення показників вакцинації дітей у громадах Львівської області з історично низьким рівнем охоплення щепленнями. Матеріали та методи. Цільова SMS-кампанія проводилася у два етапи протягом жовтня — листопада 2024 року. Абонентам мобільного зв’язку були надіслані 41 392 SMS-повідомлення. Проведено аналіз записів про вакцинацію з електронної системи охорони здоров’я за основними дитячими вакцинами (АКДП, Поліо, КПК). Для оцінки взаємозв’язку між SMS-сповіщеннями та кількістю проведених щеплень використовували коефіцієнт кореляції Пірсона та χ2-критерій. Результати. Після другого етапу SMS-розсилки середньодобова кількість вакцинацій зросла з 82 до приблизно 150 щеплень на день, із високим коефіцієнтом кореляції (r = 0,86; p = 0,0612). Конверсія становила менше 1 %, що вказує на обмежену ефективність загальних SMS-повідомлень. Водночас спостерігалося збільшення відвідуваності сайту Львівського обласного центру контролю та профілактики хвороб, що свідчить про поліпшення цифрової активності населення. Висновки. SMS-повідомлення є перспективним короткостроковим інструментом для підвищення рівнів охоплення вакцинацією, однак для поліпшення ефективності необхідно застосовувати персоналізовані та цільові стратегії інформування. Рекомендується проведення подальших досліджень із залученням більших вибірок, аналізом економічної ефективності, цифрової грамотності населення й розробкою персоналізованих повідомлень.
Background. Digital health interventions, particularly Short Message Service (SMS) notifications, have significant potential to improve healthcare outcomes, including vaccination rates. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and disruptions to healthcare infrastructure have increased the urgency for innovative strategies to maintain routine immunization services. The purpose of the study was to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of an SMS-based intervention designed to enhance childhood immunization visit rates in selected communities with historically low vaccination attendance in the Lviv Region, Ukraine. Materials and methods. A targeted SMS campaign was implemented in October-November 2024, conducted in two stages. Initial messages were sent to 41,392 mobile subscribers. Vaccination records from the electronic healthcare system were analyzed, focusing on primary childhood vaccines (DTP, Polio, MMR). Pearson’s correlation and chi-square tests were utilized to assess the relationship between SMS notifications and vaccination uptake. Results. Following the second SMS intervention, average daily vaccinations increased significantly from 82 to approximately 150 per day, with a strong correlation coefficient (r = 0.86; p = 0.0612). The conversion rate was below 1 %, suggesting limited effectiveness of generic SMS messages. Increased traffic on the Lviv Regional Center for Disease Control and Prevention website indicated enhanced digital engagement. Conclusions. SMS-based notifications show promise as short-term behavioral nudges to increase vaccination rates, yet personalization and targeted messaging strategies are necessary for improved effectiveness. Further research on larger scales, including cost-effectiveness, digital literacy assessment, and personalized message development, is recommended.
дитяче здоров’я; цифрове здоров’я; імунізаційні програми; нагадувальні системи; текстові повідомлення; охоплення вакцинацією
child health; digital health; immunization programs; reminder systems; text messaging; vaccination coverage
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Tung EL, Press VG, Peek ME. Digital health readiness and health equity. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(9):e2432733. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.32733.
- World Health Organization. Global diffusion of eHealth: making universal health coverage achievable. Report of the third global survey on eHealth. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
- Colom A. The digital divide: by Jan van Dijk. Cambridge: Polity Press; 2020, 208 p., ISBN: 978-1-509-534456. Information Communication Soc. 2020;23(11):1706-1708. doi: 10.1080/1369118x.2020.1781916.
- Andreas M, Iannizzi C, Bohndorf E, Monsef I, Piechotta V, Meerpohl JJ, Skoetz N. Interventions to increase COVID-19 vaccine uptake: a scoping review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;8(8):CD015270. doi: 10.1002/14651858.cd015270.
- Currie GE, McLeod C, Waddington C, Snelling TL. SMS-based interventions for improving child and adolescent vaccine coverage and timeliness: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2024;24(1):1753. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18900-4.
- Onigbogi O, Ojo OY, Kinnunen UM, Saranto K. Mobile health interventions on vaccination coverage among children under 5 years of age in low- and middle-income countries: a scoping review. Front Public Health. 2025;13:1392709. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1392709.
- Crawford A, Serhal E. Digital health equity and COVID-19: the innovation curve cannot reinforce the social gradient of health. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(6):e19361. doi: 10.2196/19361.
- Huf SW, Grailey K, Crespo RF, Woldmann L, Chisambi M, et al. Testing the impact of differing behavioural science informed text message content in COVID-19 vaccination invitations on vaccine uptake: a randomised clinical trial. Vaccine. 2024;42(11):2919-2926. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.03.059.
- Kagucia EW, Ochieng B, Were J, Hayford K, Obor D, O’Brien KL, Gibson DG. Impact of mobile phone delivered reminders and unconditional incentives on measles-containing vaccine timeliness and coverage: a randomised controlled trial in western Kenya. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(1):e003357. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003357.
- Mekonnen ZA, Gelaye KA, Were M, Tilahun B. Effect of mobile phone text message reminders on the completion and timely receipt of routine childhood vaccinations: superiority randomized controlled trial in northwest Ethiopia. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021;9(6):e27603. doi: 10.2196/27603.
- Beyrer C. Assessing the impact of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine on health services: crimes of war. JAMA Health Forum. 2024;5(5):e240924. doi: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.0924.
- Kim HJ, Bruni E, Gorodetska G, van den Bergh R, Bezer L, et al. Typology and implications of verified attacks on health care in Ukraine in the first 18 months of war. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024;4(5):e0003064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003064.
- World Bank Group. Mobile cellular subscriptions (per 100 people), 2023. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/IT.CEL.SETS.P2.
- National Health Service of Ukraine. Statistics on submitted declarations for selecting a primary healthcare provider. Available from: https://edata.e-health.gov.ua/e-data/dashboard/declar-stats.
- National Health Service of Ukraine. Statistics on medical records of population vaccination. Available from: https://edata.e-health.gov.ua/e-data/dashboard/immunization-stats.
- Ezeilo CO, Leon N, Jajodia A, Han HR. Use of social media for health advocacy for digital communities: descriptive study. JMIR Form Res. 2023;7:e51752. doi: 10.2196/51752.
- Carini E, Villani L, Pezzullo AM, Gentili A, Barbara A, Ricciardi W, Boccia S. The impact of digital patient portals on health outcomes, system efficiency, and patient attitudes: updated syste–matic literature review. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(9):e26189. doi: 10.2196/26189.
- Backman C, Papp R, Tonjock Kolle A, Papp S, Visintini S, et al. Platform-based patient-clinician digital health interventions for care transitions: scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2024;26:e55753. doi: 10.2196/55753.