Oral and General Health Том 5, №3, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Поширеність патології тканин пародонта в дітей із різними типами патологічного прикусу
Авторы: Лихота К.М., Ватага К.А.
Національний університет охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Стоматология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
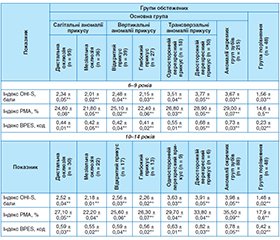
Актуальність. Умови здоров’я порожнини рота можуть негативно впливати на функціональне, соціальне та психологічне благополуччя маленьких дітей, підлітків та їхніх сімей, спричиняючи біль і дискомфорт для дитини. Карієс і захворювання пародонта є найпоширенішими хворобами зубів у дітей. Серед запальних захворювань пародонта в дитячому віці домінує хронічний катаральний гінгівіт . Значну роль у патогенезі захворювань пародонта відіграють місцеві й загальні фактори. Вплив патологічного прикусу на рівень захворювання ясень залишається невизначеним, і результати досліджень у цій галузі є суперечливими. Своєчасна функціональна діагностика змін, що відбуваються в тканинах пародонта при патології прикусу, є важливою ланкою в профілактиці захворювань пародонта під час ортодонтичного лікування. Мета. Вивчити поширеність патології тканин пародонта в дітей із різними типами патологічного прикусу. Матеріали та методи. Досліджено стан тканин пародонта в 573 дітей віком від 6 до 14 років із патологією прикусу (основна група) та 48 дітей без патології прикусу (група порівняння). Порушення прикусу оцінювали в трьох взаємно перпендикулярних площинах, а також за допомогою стоматологічного естетичного індексу (DAI). Аномалії положення окремих зубів визначали за класифікацією Лішера (Lischer’s classification). Для визначення стану ротової порожнини використовували пародонтальні й гігієнічні індекси: спрощений індекс гігієни порожнини рота (OHI-S) за Гріном — Вермілліоном (Greene-Vermillion, 1964), індекс РМА (papillary-marginal-attached, 1949), запропонований Massler і модифікований Parma, а також комбінований пародонтальний індекс Basic Periodontal Examination-Simplified (BPES). Результати. Патологія прикусу суттєво впливає на стан пародонта в дітей. У пацієнтів з аномаліями прикусу спостерігається на 30–50 % вищий ризик розвитку запальних захворювань пародонта. 60 % дітей з патологією прикусу мають незадовільний гігієнічний стан ротової порожнини, що може призводити до розвитку хронічного катарального гінгівіту. У дітей з нормальним прикусом індекс гінгівіту (GI) становить у середньому 0,5, тоді як у дітей з патологією прикусу цей показник зростає до 1,5–2,0 (45 %). У групі дітей 6–9 років найвищий індекс BPES спостерігається у разі двостороннього перехресного прикусу (0,82 ± 0,03) й аномалії окремих груп зубів (0,73 ± 0,03). Аналогічні результати отримали в групі 10–14 років. Найнижче значення BPES (0,42 ± 0,02) спостерігається у групі порівняння, що підтверджує меншу кількість захворювань тканин пародонта в дітей без патології прикусу. Висновки. Порушення прикусу разом із захворюваннями пародонта є суттєвими факторами, що негативно впливають на здоров’я порожнини рота дітей. Відхилення від нормального прикусу можуть ускладнювати гігієну порожнини рота, що призводить до накопичення зубного нальоту та розвитку запальних захворювань, таких як хронічний катаральний гінгівіт. Високий рівень поширеності гінгівіту серед дітей свідчить про важливість профілактики та раннього ортодонтичного лікування.
Background. Oral health conditions can have a negative impact on the functional, social and psychological well-being of little children, adolescents and their families, causing pain and discomfort for the child. Caries and periodontal diseases are the most common dental diseases in children. Among inflammatory periodontal diseases, chronic catarrhal gingivitis dominated in childhood. Local and general factors play a significant role in the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases. The impact of pathological occlusion on the level of gum disease remains uncertain, and the results of studies in this area are contradictory. Timely functional diagnosis of changes occurring in periodontal tissues in occlusion pathology is an important link in the prevention of periodontal diseases during orthodontic treatment. Objective: to study the prevalence of periodontal tissue pathology in children with different types of pathological occlusion. Materials and methods. The state of periodontal tissues was studied in 573 children aged 6 to 14 years with occlusion pathology (main group) and 48 children without it (comparison group). Occlusion disorders were assessed in three mutually perpendicular planes, as well as using the dental aesthetic index. Anomalies of the position of some teeth were determined according to Lischer’s classification. To evaluate the state of the oral cavity, periodontal and hygienic indices were used: simplified oral hygiene index according to Greene-Vermillion (1964), papillary-marginal-attached index (1949) proposed by Massler and modified by Parma, as well as simplified basic periodontal examination (BPES). Results. Occlusion pathology significantly affects the periodontal state in children. Patients with malocclusion have a 30–50 % higher risk of developing inflammatory periodontal diseases. 60 % of children with malocclusion have poor oral hygiene, which can lead to the development of chronic catarrhal gingivitis. In children with normal occlusion, the gingivitis index is on average 0.5, while in children with malocclusion, this figure increases to 1.5–2.0 (45 %). In the group aged 6–9 years, the highest BPES is observed in case of bilateral crossbite (0.82 ± 0.03) and anomalies of individual groups of teeth (0.73 ± 0.03). Similar results were obtained in the age group of 10–14 years. The lowest BPES (0.42 ± ± 0.02) is observed in the comparison group, which confirms the lower number of periodontal tissue diseases in children without occlusion pathology. Conclusions. Malocclusion, together with periodontal disease, are significant factors that negatively affect the oral health of children. Deviations from normal occlusion can complicate oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of dental plaque and the development of inflammatory diseases, such as chronic catarrhal gingivitis. The high prevalence of gingivitis among children indicates the importance of prevention and early orthodontic treatment.
порушення прикусу; хронічний катаральний гінгівіт; пародонтальні та гігієнічні індекси; потреба в ортодонтичному лікуванні
malocclusion; chronic catarrhal gingivitis; periodontal and hygiene indices; need for orthodontic treatment