Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 20, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив призначення метформіну та емпагліфлозину на мікробіоту кишечника в осіб із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу й гіпотиреозо
Авторы: K.A. Moskva (1), O.P. Kikhtyak (1), T.A. Kikhtiak (2), M.L. Farmaha (1), Y.L. Leshchuk (1), Y.S. Leshchuk (1)
(1) - Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
(2) - Communal Non-Commercial Enterprise of the Lviv Regional Council “Lviv Regional Clinical Hospital”, Lviv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
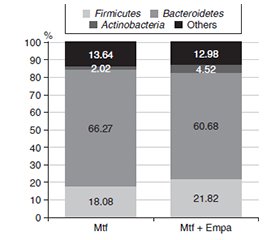
Актуальність. На сьогодні недостатньо досліджень, присвячених комбінованому впливу метформіну, емпагліфлозину й левотироксину на мікробіоту кишечника в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу (ЦД2) та гіпотиреозом. Метою дослідження було вивчити, як комбінація метформіну й емпагліфлозину впливає на склад кишкової мікробіоти в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу та гіпотиреозом. Матеріали та методи. Ми залучили 47 пацієнтів, які отримують замісну гормонотерапію левотироксином у стабільній дозі впродовж останніх двох років, із вперше діагностованим ЦД2. Усі хворі були розділені на дві групи і отримували або тільки метформін, або метформін у комбінації з емпагліфлозином упродовж шести місяців. До та після лікування вимірювали метаболічні та гормональні показники, зразки калу аналізували за допомогою ПЛР-секвенування. Результати. Дослідження показало, що в обох групах після терапії спостерігалося покращення показників вуглеводного обміну, ліпідного профілю та печінкових трансаміназ. Група, яка отримувала метформін у поєднанні з емпагліфлозином, мала вірогідне зниження рівня глюкози, глікованого гемоглобіну й коефіцієнта атерогенності, ніж група, яка отримувала лише метформін. Ми виявили, що комбінована терапія приводила до зниження рівнів Firmicutes і збільшення кількості Actinobacteria, а також підвищувала співвідношення групи Bacteroides fragilis до Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Висновки. Дослідження вперше показує, що комбінація метформіну, емпагліфлозину та левотироксину може безпосередньо впливати на склад кишкової мікробіоти в пацієнтів із ЦД2 і гіпотиреозом. Указані зміни можуть бути важливими для лікування цієї когорти хворих та потребують подальших досліджень.
Background. There is a lack of studies focusing on the combined impact of metformin, empagliflozin, and levothyroxine on the gut microbiota in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and hypothyroidism. The purpose of the study was to examine how the combination of metformin and empagliflozin affects gut microbiota composition in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypothyroidism. Materials and methods. We enrolled 47 patients who have been receiving hormone replacement therapy with levothyroxine at a stable dose over the past 2 years and were newly diagnosed with T2DM. All participants were divided into two groups and received either metformin alone or metformin plus empagliflozin for 6 months. Metabolic and hormonal parameters were measured before and after treatment, and stool samples were analyzed using PCR sequencing. Results. The study found that in both groups, there was an improvement in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid profile, and liver transaminases after treatment. The group treated with metformin plus empagliflozin had a more significant reduction in glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and atherogenicity coefficient than the group treated with metformin alone. We also found that combination therapy resulted in lower levels of Firmicutes and an increase in the number of Actinobacteria, as well as a higher ratio of Bacteroides fragilis to Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Conclusions. The study shows for the first time that the combination of metformin, empagliflozin, and levothyroxine can directly affect the gut microbiota composition in patients with T2DM and hypothyroidism. These changes may be necessary for treating this cohort of patients and require further investigation.
цукровий діабет; гіпотиреоз; метформін; емпагліфлозин; кишкова мікробіота
diabetes mellitus; hypothyroidism; metformin; empagliflozin; gut microbiota
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Petakh P, Kamyshna I, Kamyshnyi A. Effects of metformin on the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Mol Metab. 2023 Nov;77:101805. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101805.
- Madej A, Senat H, Grabowska P, Bolla P, Senat A, et al. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Education, Health and Sport. 2024;55:38-51. doi: 10.12775/JEHS.2024.55.003.
- Zhang L, Chu J, Hao W, Zhang J, Li H, et al. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Association, Mechanism, and Translational Applications. Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Aug 17;2021:5110276. doi: 10.1155/2021/5110276.
- Sowmiya T, Silambanan S. Association of Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023;19(7):e211122211066. doi: 10.2174/1573399819666221121104542.
- Tang WH, Kitai T, Hazen SL. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ Res. 2017 Mar 31;120(7):1183-1196. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715.
- Kappel BA, Lehrke M. Microbiome, diabetes and heart: a novel link? Herz. 2019 May;44(3):223-230 (in German). doi: 10.1007/s00059-019-4791-x.
- Moskva K, Kikhtyak O, Lapovets L, Urbanovych A. Changes in the gut microbiota under the influence of metformin, pioglitazone, and levothyroxine in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism. Problems of Endocrine Pathology. 2022;79(4):45-51. doi: 10.21856/j-PEP.2022.4.06.
- Zhang Q, Hu N. Effects of Metformin on the Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Dec 16;13:5003-5014. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S286430.
- Almugadam BS, Liu Y, Chen SM, Wang CH, Shao CY, et al. Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Individuals and the Confounding Effect of Antidiabetic Agents. J Diabetes Res. 2020 Sep 28;2020:7253978. doi: 10.1155/2020/7253978.
- Liu Z, Liao W, Zhang Z, Sun R, Luo Y, et al. Metformin Affects Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity Associated with Amelioration of Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 21;12:640347. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.640347.
- Brahe LK, Le Chatelier E, Prifti E, Pons N, Kennedy S, et al. Dietary modulation of the gut microbiota — a randomised controlled trial in obese postmenopausal women. Br J Nutr. 2015 Aug 14;114(3):406-17. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515001786.
- Zhou YD, Liang FX, Tian HR, Luo D, Wang YY, Yang SR. Mechanisms of gut microbiota-immune-host interaction on glucose re–gulation in type 2 diabetes. Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1121695. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1121695.
- Lovic D, Pittaras A, Kallistratos M, Tsioufis C, Grassos C, et al. Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Potential Cardiovascular and Mortality Benefits. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;18(2):114-119. doi: 10.2174/1871529X18666180227102137.
- Di Segni A, Braun T, BenShoshan M, et al. Guided Protocol for Fecal Microbial Characterization by 16S rRNA-Amplicon Sequencing. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 2018 Mar(133). doi: 10.3791/56845.
- Djuryak V, Mikheev A, Sydorchuk L, Pankiv I. The state of the colon microbiome in women with gestational diabetes. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2023;19(4):284-289. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.19.4.2023.1287.
- Silamiķele L, Silamiķelis I, Ustinova M, Kalniņa Z, Elbere I, et al. Metformin Strongly Affects Gut Microbiome Composition in High-Fat Diet-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mouse Model of Both Sexes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 19;12:626359. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.626359.
- Moskva K, Kikhtyak O, Lapovets L, Lanyush F. Comparison of changes in the gut microbiota influenced by combinations of liraglutide with metformin and pioglitazone with metformin in overweight patients with diabetes. Diabetologia. 2023;66(Suppl 1):331. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-05969-6.
- Vallianou NG, Stratigou T, Tsagarakis S. Metformin and gut microbiota: their interactions and their impact on diabetes. Hormones (Athens). 2019 Jun;18(2):141-144. doi: 10.1007/s42000-019-00093-w.
- Doğan D, Çelik T. Research trends on the gut micro–biota in endocrine metabolism: a thematic and bibliometric analysis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 22;14:1371727. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1371727.
- Miloslavsky D, Koval S. Prospects for probiotics use as the gut microbiota modulators in obesity (literature review). Internatio–nal Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2022;18(6):358-364. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.18.6.2022.1207.