Архив офтальмологии Украины Том 11, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Можливості прогнозування запальних ускладнень після факоемульсифікації у хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го тип
Авторы: Жабоєдов Д.Г., Кирпичников О.В.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Медичний офтальмологічний центр «Зір 100%», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Офтальмология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
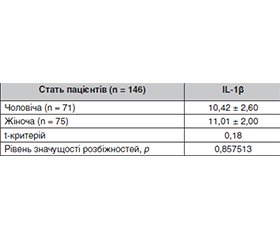
Актуальність. Катаракта є одним з найчастіших очних ускладнень, які супроводжують цукровий діабет. На сьогодні факоемульсифікація з імплантацією задньокамерної інтраокулярної лінзи (ІОЛ) — це стандарт лікування катаракти. Слід зазначити роль імунологічних порушень у патогенезі запальної реакції, що виникає у відповідь на операційну травму. На думку низки дослідників, при оцінці балансу цитокінів важливим є не тільки зміна концентрації інтерлейкінів у біологічних рідинах, але й співвідношення цитокінів, що мають про- та протизапальну активність, здатних стимулювати гуморальну або клітинну ланку імунної системи. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебували 80 пацієнтів (146 очей) із катарактою, хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу, яким виконувалася факоемульсифікація з імплантацією ІОЛ. Під час проведення хірургічного втручання у пацієнтів забирали внутрішньоочну рідину одноразовим інсуліновим шприцом через парацентез рогівки в обсязі 0,1–0,2 мл для дослідження вмісту інтерлейкінів (IL-1β, IL-8, IL-10). Результати. При дослідженні IL-1β у внутрішньоочній рідині у хворих із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу після хірургічного лікування катаракти було встановлено, що його рівень коливався від 0,1 до 110,7 пг/мл і в середньому становив 10,72 пг/мл, IL-8 — від 1,6 до 386,4 пг/мл і в середньому становив 109,2 пг/мл, IL-10 — від 0,64 до 10,2 пг/мл і в середньому становив 3,37 пг/мл. Встановлено статистично значущий зв’язок вмісту IL-1β, IL-8, IL-10 у внутрішньоочній рідині із розвитком запальних ускладнень після хірургії катаракти у хворих на цукровий діабет, а саме при підвищенні рівнів IL-1β, IL-8 та зниженні рівня IL-10 статистично значуще підвищується частота запальних ускладнень. При рівні IL-1β 11,2–13,7 пг/мл частота запальних ускладнень статистично значуще збільшується в 2 рази, при рівні 14,1–110,7 — у 5 разів проти рівня 0,1–0,8 пг/мл (χ2 = 64,33; р < 0,001). При рівні IL-8 10,3–178,3 пг/мл частота запальних ускладнень статистично значуще збільшується в 3 рази, при рівні 196,0–386,4 — у 5 разів проти рівня 1,6–7,4 пг/мл (χ2 = 41,56; р < 0,001). При рівні IL-10 0,64–0,9 пг/мл частота запальних ускладнень статистично значуще збільшується в 6 разів проти рівня 5,1–6,2 пг/мл та в 5 разів — проти рівня 7,3–10,2 пг/мл (χ2 = 8,66; р = 0,014).
Background. Cataract is one of the most frequent eye complications that accompany diabetes. Currently, phacoemulsification with a posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation is the standard of care for cataracts. It should be noted the role of immunological disorders in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory reaction that occurs in response to surgical trauma. According to some researchers, when assessing the balance of cytokines, not only a change in the concentration of interleukins in biological fluids is important, but also the ratio of cytokines with pro- and anti-inflammatory activity, which can stimulate the humoral or cellular link of the immune system. Materials and methods. Eighty patients (146 eyes) with cataract on the background of type 2 diabetes who underwent phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation were under observation. During surgery, intraocular fluid was taken from patients with a disposable insulin syringe through corneal paracentesis in the amount of 0.1–0.2 ml to evaluate the content of interleukins (IL-1β, IL-8, IL-10). Results. When studying IL-1β in the intraocular fluid of patients with type 2 diabetes after surgical treatment of cataracts, it was found that it ranged from 0.1 to 110.7 pg/ml and averaged 10.72 pg/ml, IL-8 level was from 1.6 to 386.4 pg/ml and averaged 109.2 pg/ml, IL-10 was from 0.64 to 10.2 pg/ml and averaged 3.37 pg/ml. A statistically significant relationship was found between the content of IL-1β, IL-8, IL-10 in the intraocular fluid and the development of inflammatory complications after cataract surgery in patients with diabetes, namely, with an elevation of IL-1β, IL-8 levels and a decrease in IL-10, the frequency of inflammatory complications increased statistically significantly. When IL-1β content is 11,2–13,7 pg/ml, the frequency of inflammatory complications increases statistically significantly by 2 times; at the level of 14.1–110.7 pg/ml, by 5 times compared to 0.1–0.8 pg/ml (χ2 = 64.33; p < 0.001). With IL-8 level of 10.3–178.3 pg/ml, the frequency of inflammatory complications increases statistically significantly by 3 times; at the level of 196.0–386.4 pg/ml, by 5 times compared to 1.6–7.4 pg/ml (χ2 = 41.56; p < 0.001). When IL-1β content is 0.64–0.9 pg/ml, the frequency of inflammatory complications is statistically significantly increases by 6 times compared to 5.1–6.2 pg/ml and by 5 times compared to the level of 7.3–10.2 pg/ml (χ2 = 8.66; p = 0.014).
факоемульсифікація; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; запальні ускладнення; прогнозування
phacoemulsification; type 2 diabetes; inflammatory complications; prognosis
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Grzybowski A., Kanclerz P., Huerva V., Ascaso F.J., Tuumi–nen R. Diabetes and Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery: Difficulties, Risks and Potential Complications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019 May. 8(5). 716.
- Peterson S.R., Silva P.A., Murtha T.J., Sun J.K. Cataract surgery in patients with diabetes: management strategies. InSeminars in Оphthalmology. 2018 Jan 2. 33 (1). 75-82.
- Haddad N.M., Sun J.K., Abujaber S., Schlossman D.K., Silva P.S. Cataract surgery and its complications in diabetic patients. InSeminars in Оphthalmology. 2014 Sep 1. 29 (5-6). 329-337.
- International Diabetes Federation. 2015. IDF Diabetes Atlas 7 th Edition. Brussels, Belgium. Available from: https://idf.org/e-library/epidemio–logy-research/diabetes-atlas/13-diabetes-atlas-se–venth-edition.html.
- Kaze A.D., Yuyun M.F., Ahima R.S., Sachdeva M.M., Echouffo-Tcheugui J.B. Association of heart rate variability with progression of retinopathy among adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2022 Jul. 39(7). e14857.
- Mohammadi S.F., Hashemi H., Mazouri A., Rahman A.N., Ashrafi E., Mehrjardi H.Z. et al. Outcomes of cataract surgery at a referral center. Journal of Ophthalmic & Vision Research. 2015 July. 10(3). 250.
- Raman R., Pal S.S., Adams J.S., et al. Prevalence and risk factors for cataract in diabetes: Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology and Molecular Genetics Study, report no. 17. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010. 51(12). 6253-6261.
- Parkhomenko G., Mogilevsky S. Comparative evaluation of the duration of phacoemulsification of cataracts with a dense nucleus at normal and high intraocular pressure. In: Refraction Plenary'21: scientific and practical conference with international participation on October 29-30, 2021: collection of proceedings. Еd. by S.O. Rykov. Kyiv, 2021. 75-77.
- Draganic V., Vukosavljevic M., Milivojevic M., et al. Evolution of cataract surgery: smaller incision — less complications. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2012. 69(5). 385-388.
- Park Y.G., Jee D., Kwon J.W. Aqueous Humor Cytokine Le–vels in Diabetic Macular Edema Patients with Cotton-Wool Spots. J. Diabetes Res. 2019 Dec 21. 2019. 8137417.
- Anaya J.M., Shoenfeld Y., Rojas-Villarraga A., Levy R.A., Cervera R., editors. Autoimmunity: From Bench to Bedside [Internet]. Bogota (Colombia): El Rosario University Press; 2013 Jul 18. PMID: 29087650.
- Arango Duque G., Descoteaux A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014 Oct 7. 5. 491.
- Tamhane M., Cabrera-Ghayouri S., Abelian G., Viswanath V. Review of Biomarkers in Ocular Matrices: Challenges and Opportunities. Pharm. Res. 2019. 36. 40.
- Vujosevic S., Simó R. Local and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers of Diabetic Retinopathy: An Integrative Approach. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017. 58. bio 68–bio75.
- Lv J., Cao C.J., Li W., Li S.L., Zheng J., Yang X.L. Tear inflammation related indexes after cataract surgery in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Clin. Cases. 2023 Jan 16. 11(2). 385-393.
- Obadă O., Pantalon A.D., Rusu-Zota G., Hăisan A., Lupuşoru S.I., Constantinescu D., Chiseliţă D. Aqueous Humor Cytokines in Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 8. 58(7). 909.
- Krasnozhan O.V., Lutsenko N.S., Zhaboyedov D.G., Efimenko N.F. Features of the systemic cytokine status in cataracts in combination with moderate and high myopia. Archives of Ophthalmology of Ukraine. 2020. 8 (1). 54-59.